Chrome ore, mainly chromite (FeCr₂O₄), is vital for making ferrochrome used in stainless steel. This article explains the chrome ore mining and processing steps—exploration, extraction, and beneficiation—and highlights Xinhai Mining’s advanced solutions that boost recovery, cut waste, and support key industries like metallurgy, refractories, and chemicals.
First things first, miners hunt for chrome ore deposits. They map out the land, grab some rock samples, and test them to figure out the ore’s quality. They also check how deep it is and if it’s easy to get to. If the site looks good, they run the numbers to see if it’s worth the cash to mine it. This part’s like detective work—gotta make sure the ore’s worth chasing.
There’s two main ways to get chrome ore out: open-pit or underground mining. Open-pit’s the go-to when the ore’s near the surface. It’s quicker and doesn’t cost as much. But if the ore’s buried deep, underground mining’s the only option. Miners pick based on things like how deep the ore sits, what the nearby rocks are like, and how it’ll affect the environment. They also keep an eye on costs, ‘cause nobody wants to lose money.
Whether it’s open-pit or underground, the process starts with drilling holes in the rock. Then, they blast it with explosives to break it into smaller pieces. After that, trucks or conveyor belts haul the ore to a processing plant. It’s noisy, messy work—think clouds of dust and loud booms. I read about a mine in Kazakhstan where they use trucks that can carry 150 tons of ore at once. That’s some serious heavy lifting!
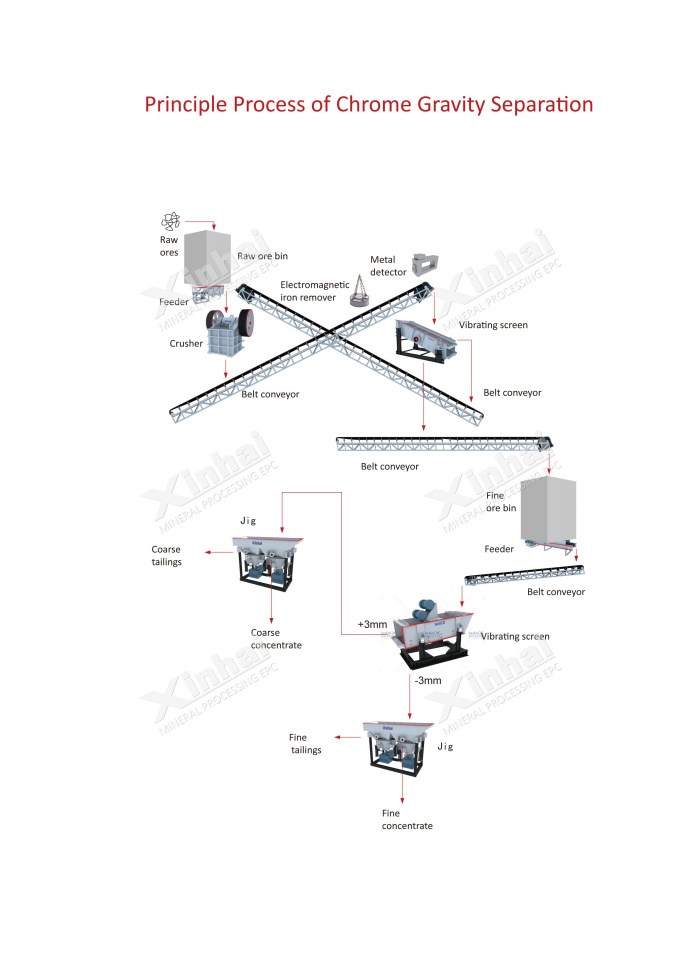
Once the ore’s out of the ground, it’s time to break it down. Big machines, like jaw crushers, smash the ore into smaller chunks. Then, secondary crushers make those chunks even smaller. After that, grinding mills turn the ore into a fine powder. This step’s a big part of chrome ore mining processing—it gets the ore ready for the next bit, where the good stuff gets separated.
Most chrome ore needs cleaning up to get the valuable bits. The main trick in chrome ore mining processing is gravity separation. Tools like washboxes (or jiggers, as some call ‘em), shaking tables, and spiral classifiers do the job. Here’s the usual flow: after crushing and grinding, the ore gets washed. A spiral classifier sorts it based on how heavy the particles are and how fast they sink in liquid. Then, jigs and shaking tables clean it more. Finally, a spiral chute sorts out the fine powder.
Now, some ores are a pain—maybe they’re too fine or mixed with weird stuff. In those cases, miners might try flotation or magnetic separation, but only if lab tests say it’s worth it. For example, in a South African mine, they switched to flotation for super-fine ore and bumped their recovery up by 12%. That’s the kind of tweak that makes a difference!
After concentrating the ore, it’s usually soaked. Miners use thickeners or filters to get rid of the water. The damp ore then goes into dryers—think big spinning drums or fluidized beds—to dry out. Once it’s dry, they screen it to make sure all the pieces are the right size. Then it’s packed up, ready to ship or head to a factory for more chrome ore mining processing, like turning it into ferrochrome for steel.
Xinhai’s making waves in chrome ore mining processing. They don’t just use one-size-fits-all methods—they study the ore closely and pick the best way to handle it. Could be gravity separation, flotation, or magnetic separation, depending on what their tests show. It’s all about getting the most chromium out while keeping things smooth.
One smart move Xinhai makes is tweaking the grinding process. They get the particle size just right to pull out more chromium. In one chromite plant, they worked with ore that had a grade over 30%—pretty rich! There were leaner ores nearby, too. After digging into the details, they set up a process with strong magnetic separation to toss out the junk, then used shaking tables to sort the grains. At a grinding size of -200 mesh 60%, they hit a concentrate grade of 39.9% and a recovery rate of 64.56%. That’s solid! Plus, it cuts down on waste, which is great for the planet.
Chromium’s everywhere in industry. Here’s where it shines:
Metallurgy: Chromium makes steel tough and rust-free. Think shiny kitchen sinks or bridges that don’t corrode.
Refractory Industry: Chromite bricks handle insane heat, so they’re used in furnaces for steel or glass.
Chemical Industry: Chromium’s in colorful paints, leather tanning, and wood preservatives.
Aerospace & Automotive: Chromium’s durability is key for jet engines or car parts that need to last.
It’s wild how much we rely on chrome ore mining processing for stuff we use every day!
Real-world cases show how chrome ore mining processing plays out. Xinhai ran a chromite plant with rich ore (over 30% grade) and some leaner stuff nearby. After testing, they went with magnetic separation to ditch the waste, then shaking tables to sort the grains. This setup let them handle all kinds of ore without losing steam. At -200 mesh 60%, they got a concentrate grade of nearly 40% Cr₂O₃. That’s the kind of result that keeps factories happy.
Another example’s from a mine in India. They had ore with tricky fine particles, so they mixed gravity separation with a touch of flotation. The payoff? A 9% jump in recovery compared to old methods. These stories show how smart planning and new tech can make chrome ore mining processing way better. It’s not always smooth—sometimes the ore’s a mess, and you lose a bit—but these tricks are changing the game.
All in all, chrome ore mining processing is a big job, but it’s worth it. From digging up rocks to making shiny steel, every step counts. Companies like Xinhai are pushing things forward, and it’s pretty cool to see how they turn raw dirt into something that powers our world.