If you want to know more information (such as product/process price, etc.), please contact us 24-hour telephone
Nickel sulfide ore in Africa shows up mostly in spots like South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Botswana. These places hold a bunch of it, and each has its own quirks. For example, in Zimbabwe's Great Dyke, nickel often comes as a side product from platinum digs, with grades dipping as low as 0.5% to 1.5% in some spots. Over in Botswana's Selebi-Phikwe area, you find richer pockets, sometimes hitting 2% nickel mixed with copper. South Africa's Bushveld Complex mixes things up too, with nickel tied to thick layers of rock that make digging tougher but rewarding.

Key traits of these ores include:
Variable grades: You get surface bits that have oxidized, blended with fresh primary ores. Nickel levels swing from 0.8% up to 3.5%, depending on the site. Take the Nkomati mine in South Africa—it pulls about 1.2% nickel on average, but deeper zones push closer to 2.5%.
Complex associated metals: These ores pack extras like copper, cobalt, and even bits of gold or platinum. In Zimbabwe's Trojan mine, for instance, nickel shares space with up to 1% copper and traces of PGEs that add real value.
High hardness: The rock's tough, so you need sturdy crushers that won't wear out fast. Miners in Botswana report their gear lasting half as long here compared to softer spots elsewhere.
Key evaluation points:
Exploration: Grab a portable XRF gadget to check Ni, Co, and S levels quick on-site. It's a game-changer in remote Zimbabwe bush, where you can scan samples in minutes and spot hot zones without hauling everything to a lab.
Beneficiation testing: Mix flotation with magnetic pulls to test how much you can recover. In a South African pilot run, this combo hit 88% nickel pull from low-grade feed—solid proof it works here.

Economic modeling: Factor in LME nickel prices, which hovered around $18,000 per ton last year, plus local costs like fuel at $1.20 a liter in Botswana. Skip that, and your numbers flop.
Working these African ores feels like a puzzle sometimes—rich rewards, but you gotta watch the tricks the ground plays. From my chats with old-timers in the field, the variable stuff keeps everyone on their toes.
Here's a straightforward flow for handling nickel sulfide ore: Start with primary crushing to break big chunks. Then grind it fine. Next, run batch flotation to grab the goodies. Follow with concentration to boost purity. End with dewatering the tailings so they're not a sloppy mess.
But Africa throws curveballs, so tweak things smart. Power grids flicker out often—think Zimbabwe's blackouts that drag on for days. Water's tight too, especially in dry Botswana stretches. And finding skilled hands? Not always easy in remote digs.
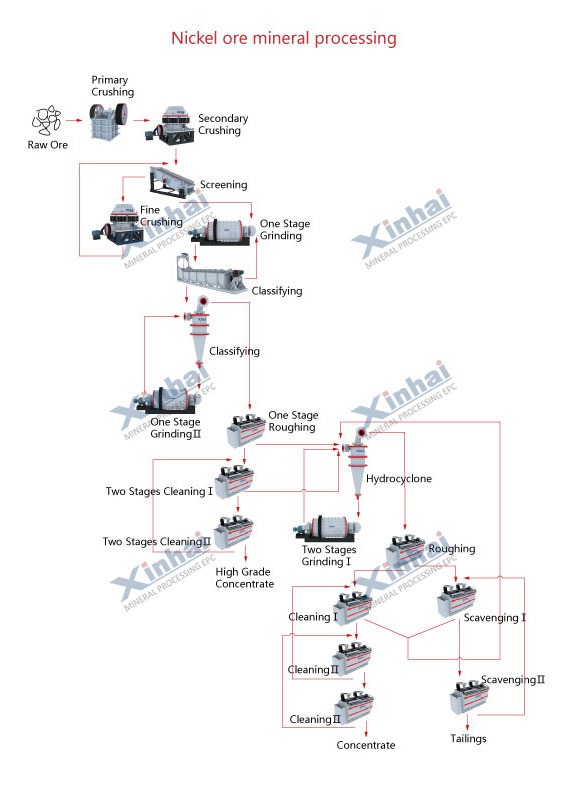
Optimization steps for African setups:
Unstable power supply: Pair diesel generators with variable speed drives on the mills. At a Zimbabwe project, this kept things humming through a two-week outage, saving $150,000 in lost time.
Water scarcity: Set up closed-loop recycling with cyclones and thickeners pulling back at least 85%. A South African crew reused 90% of their water last season, dodging fines and keeping ops smooth.
Limited operators: Go automated with PLC or DCS controls on big gear. In Botswana, one mine cut training needs by half, letting locals run complex stuff with basic oversight.
Low-grade stuff—say under 1% nickel—needs clever tricks to make it pay. Don't just grind harder; think smarter.
Process tweaks: Blend collectors like xanthate and mercaptan in flotation. It sticks better to those shy particles. Add flash flotation for chunky bits right after grinding. At Nkomati, this bumped recovery from 75% to 92% on 0.8% feed. Pretty neat how a small change flips the script.
Equipment upgrades: Swap in High-Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGR) to free up 20–30% more metal without extra energy. For fines, mechanical cells like XCF or KYF snag those tiny bits. A Zimbabwe test site saw grades jump from 1.2% to 2.8% concentrate—proof it delivers.
I've seen low-grade runs turn into cash cows when folks nail these steps. It's not magic, just good sweat and tweaks.
| Process Stage | Equipment | Function | Selection Criteria | African Adaptation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crushing | Jaw Crusher + Cone Crusher | Reduce ore to ≤25mm | High manganese steel liners (≥8,000h) | Resistant to hard ores; reduces downtime |
| Grinding | Overflow Ball Mill + Cyclone | Achieve 75% passing 200 mesh | Variable frequency drive (15–20% energy saving) | Mitigates unstable power supply |
| Flotation | Mechanical Flotation Cell | Separate sulfide minerals from gangue | 120% standby capacity | Adaptable to variable ore grades |
| Dewatering | High-Rate Thickener + Filter Press | Reduce concentrate moisture<12% | Ceramic filter plates (3x lifetime) | Reduces import costs for spare parts |
| Tailings | Screening + Slurry Pump Dry Stacking | Tailings utilization >90% | Modular design | Quick deployment in remote areas |
Xinhai Mining's EPCM+O setup— that's Engineering plus Procurement plus Construction Management plus Operation—tackles Africa's mining headaches head-on. It's like having a full team in your corner, from blueprint to first pour.
Engineering: Whip up 3D models to dodge size slip-ups from spotty ground data. In a Zimbabwe greenfield, this caught a 15% capacity gap early, saving rework headaches.
Procurement: Source worldwide to trim gear costs 30–50%. Botswana buyers nabbed Chinese crushers 40% cheaper, shipped direct, no middlemen gouge.
Construction: Train locals under pro eyes to speed things 20%. A South African build wrapped eight months ahead, thanks to community crews who knew the turf.
Operation: Remote smarts plus a local parts depot mean fixes in under 24 hours, slashing upkeep 40%. One mine cut breakdowns by 60%, keeping output steady.
This model's a buffer against the wild cards—power dips, supply snags, you name it. It's not foolproof, but it sure beats flying solo.

Picture a mid-tier nickel project in Zimbabwe's Midlands. Using EPC+M+O, they sourced modular plants locally, dodging import duties and delays. CAPEX dropped $22 million— that's cash back in pockets for expansions.
Startup? Clocked 14 months, not the usual 22. Crews hit full tilt faster, with fewer teething pains. OPEX? Health checks on gear trimmed yearly costs 18%, or about $3.2 million saved. It's real-world wins like this that make the model shine.
Ready to dive in? Start smart.
Feasibility study: Run pilot tests to see if your ore plays nice. A Botswana group tested 500 tons and nailed 85% recovery—key data before big spends.
Cost analysis: Stack EPCM+O against old-school over 10 years. One calc showed 25% lower lifecycle costs, factoring fuel hikes and fixes.
Risk management: Ask for supplier tales from African jobs, plus stock checks on parts. A South African buyer grilled on spares and avoided a three-month shutdown.
These steps keep surprises low. Chat early, test often—it's how pros roll.
Africa's nickel sulfide ores pack plenty—abundant and full of extras like cobalt that boost the pot. But they're tricky, with hard rock, spotty power, and dry spells testing your grit. Smart processing flows, tough gear, and the EPC+M+O way can lift recoveries to 90% plus and trim costs sharp.
It's rewarding work, though. Seeing a rough site hum with output? That's the buzz that keeps folks coming back.
Contact us or learn more about Xinhai Mining + nickel sulfide ore processing customization services for project-specific solutions and technical support.